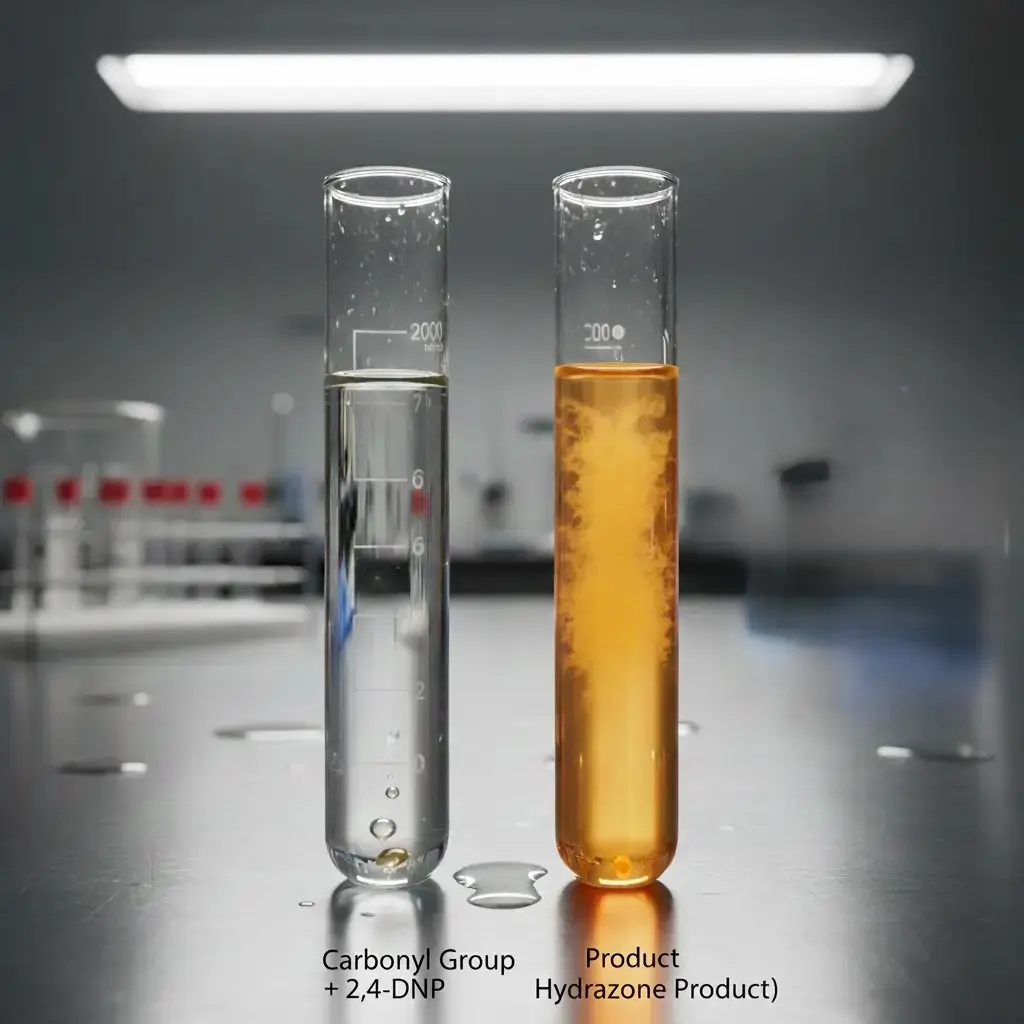
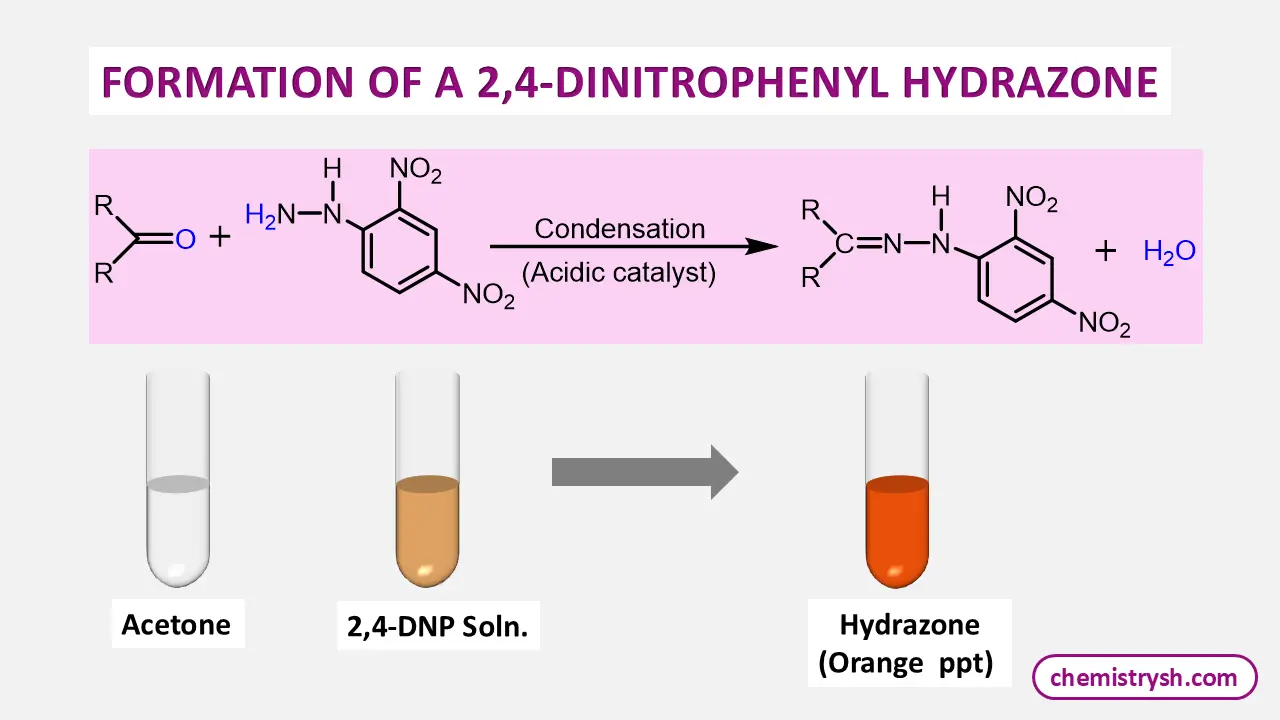
The 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4-DNPH) test, also known as Brady’s test, is a classical qualitative test used in organic chemistry to detect the presence of carbonyl functional groups in organic compounds, specifically aldehydes and ketones.
The reagent, 2,4-DNPH, reacts with the carbonyl group (C=O) to form a solid, colored 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone derivative.
The appearance of a yellow, orange, or red precipitate confirms the presence of a carbonyl compound.

What is 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine?
2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine is an aromatic hydrazine derivative containing two electron-withdrawing nitro groups attached to a benzene ring. It is usually used in an acidic alcoholic medium, which enhances its reactivity toward carbonyl compounds. The presence of nitro groups increases the stability and color intensity of the reaction product.
Principle of the 2,4-DNP Test
The test works on a condensation reaction between the carbonyl group of an aldehyde or ketone and 2,4-DNP. In an acidic medium, the carbonyl carbon becomes more reactive and undergoes nucleophilic attack by the hydrazine group.
2,4‑DNPH reacts with aldehydes and ketones to form solid 2,4‑dinitrophenylhydrazone derivatives, producing yellow/orange/red precipitates.
General Reaction:
R‑CO‑R’ + H₂NNHC₆H₃(NO₂)₂ → R‑C=N‑NH‑C₆H₃(NO₂)₂ + H₂O
🧪Procedure
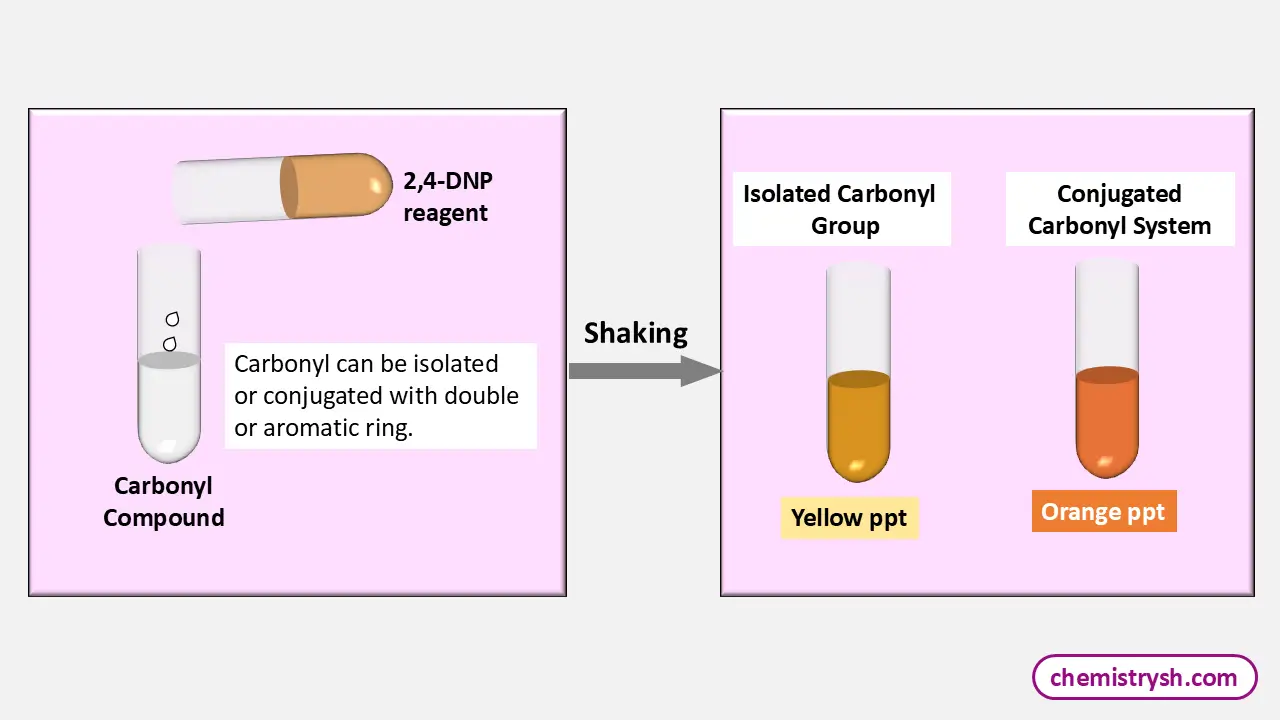
The color depends on the structure of the aldehyde or ketone.
Aliphatic carbonyls → yellow precipitate
Aromatic or conjugated carbonyls → orange to red precipitate
Observation and Result
A positive 2,4-DNP test is confirmed by the formation of a yellow, orange, or red precipitate. The intensity of the color depends on the nature of the carbonyl compound. Aliphatic aldehydes and ketones usually give a yellow precipitate, while aromatic carbonyl compounds form deeper orange or red precipitates due to greater conjugation.
If no precipitate is formed, the test is considered negative, indicating the absence of aldehyde or ketone groups.
|
Compound Type |
2,4-DNP Test Result |
|
Formaldehyde |
Yellow ppt |
|
Acetone |
Yellow ppt |
|
Benzaldehyde |
Orange ppt |
|
Acetophenone |
Orange-red ppt |
|
Crotonaldehyde (unsaturated) |
Deep red ppt |
|
Alcohols / Acids |
No reaction |
Why Aldehydes and Ketones Respond to 2,4-DNP
Aldehydes and ketones readily give the 2,4-DNP test because they contain a polar and reactive carbonyl group. The carbonyl carbon is electron-deficient and easily attacked by nucleophiles such as the hydrazine group. This reactivity leads to the formation of a stable hydrazone derivative, which separates out as a precipitate.
Compounds That Do Not Give the Test
Alcohols, carboxylic acids, esters, and ethers do not respond to the 2,4-DNP test because they lack a free carbonyl group capable of undergoing condensation. As a result, no precipitate is formed in these cases.
Role of 2,4-DNP in Identification of Carbonyl Compounds
The 2,4-DNP test is widely used not only for detection but also for identification of unknown aldehydes and ketones. The hydrazone derivatives formed are crystalline solids with sharp melting points. By comparing the melting point of the derivative with known values, specific carbonyl compounds can be identified in organic analysis
Importance and Applications
Complementary Tests for 2,4-DNP test Reaction
- Tollens’ Test (Silver Mirror Test): Distinguishes aldehydes from ketones by forming a shiny silver layer on the test tube wall.
- Fehling’s Test: Identifies aliphatic aldehydes (like glucose) by producing a brick-red precipitate of copper(I) oxide.
- Lucas Test: Differentiates between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols based on how quickly the solution turns cloudy (turbid).
Viva questions
- What does the 2,4-DNP test detect?
- Why does a precipitate form in this test?
- What colors are observed for aldehydes and ketones?
- Why do alcohols not give this test?
- What is the principle behind hydrazone formation?
- What is the reagent used in this test?
- Why is the reagent kept acidic?
- What is Brady’s reagent?
Multiple Choice Questions
MCQ 1
The 2,4‑DNPH test is used for detecting which group?
A. Hydroxyl
B. Carbonyl
C. Carboxyl
D. Amide
MCQ 2
2. A positive DNPH test gives:
A. Blue solution
B. Yellow/orange/red precipitate
C. White fumes
D. No change
MCQ 3
3. Which of the following gives a positive DNPH test?
A. Methanol
B. Ethanoic acid
C. Propanone
D. Methylamine
MCQ 4
4. DNPH reacts with carbonyl compounds to form:
A. Esters
B.Hydrazones
C. Alcohols
D. Amines
MCQ 5
5. DNPH test cannot distinguish between:
A. Aldehydes
B. Ketones
C. Aldehydes & ketones
D. Alcohols
MCQ 6
6. Which compound will not give 2,4-DNP test?
A. Acetone
B. Ethanal
C. Ethanol
D. Benzaldehyde
FAQ’s
References
- Brady, O. L. (1931). A simple qualitative test for aldehydes and ketones. Journal of the Chemical Society.
- Furniss, B. S., et al. Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry.
- Reusch, W. (n.d.). Carbonyl compound identification. MCC Organic Chemistry.
- THE IDENTIFICATION OF CARBONYL COMPOUNDS BY USE OF 2,4-DINITROPHENYLHYDRAZINE