The KMnO₄ Test, also known as Baeyer’s test, is a classical chemical test used in organic chemistry to identify certain functional groups in organic compounds.
It utilizes potassium permanganate (KMnO₄), a strong oxidizing agent, to detect unsaturation (carbon–carbon double bonds) and aldehydes.
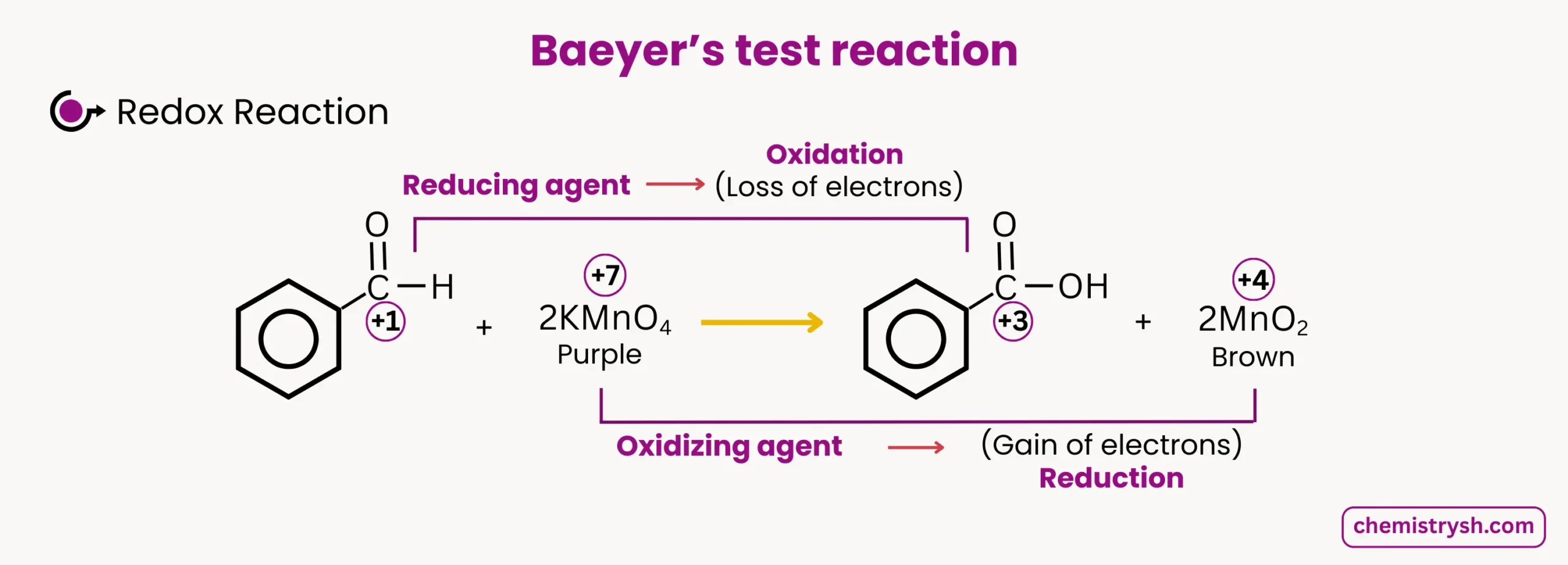
A positive reaction is indicated by the disappearance of the purple color of KMnO₄ and the formation of a brown precipitate of manganese dioxide (MnO₂). This simple reaction serves as an effective qualitative test in laboratories and educational settings.

Principle of KMnO₄ Test
The KMnO₄ test is based on the oxidizing ability of potassium permanganate. In alkaline medium, KMnO₄ oxidizes organic compounds and is reduced from Mn⁷⁺ (purple) to Mn⁴⁺ (brown precipitate, MnO₂).
- Alkenes: Double bonds are oxidized to vicinal diols.
- Aldehydes: Oxidized to carboxylic acids.
The key observation is the fading of the purple color of KMnO₄ accompanied by the formation of a brown precipitate, indicating the oxidation of the organic substrate. Saturated compounds generally do not react, so the purple color remains unchanged.
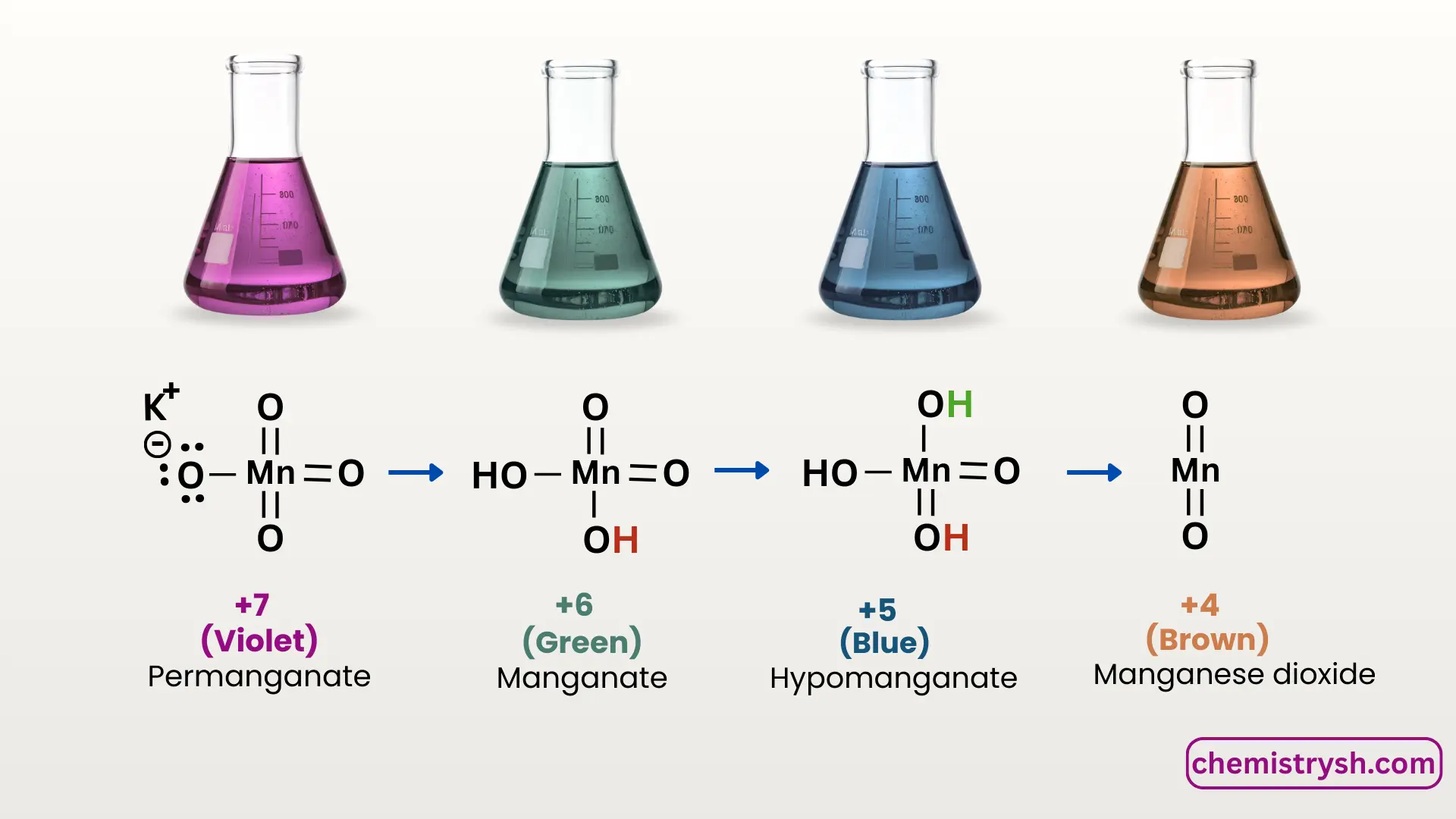
Oxidation States of KMnO₄ and Corresponding Colors
|
Oxidation state of Mn |
Chemical Species |
Color in Solution |
Solution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
+7 |
Permanganate (MnO₄⁻) |
Purple/ violet |
Original KMnO₄ solution | |
|
+6 |
Manganate (MnO₄²⁻) |
Green |
Intermediate in alkaline medium | |
|
+5 |
MnO₄³⁻ |
Blue |
Very unstable | |
|
+4 |
MnO₂ |
Brown/ Black precipitate |
Oxidation product | |
|
+2 |
Mn²⁺ |
Colorless / Pale Pink |
End product in acidic conditions |
In the KMnO₄ test, the most common reduction observed is Mn⁷⁺ → Mn⁴⁺, which corresponds to the purple to brown color change.
Chemical Reactions and Functional Groups
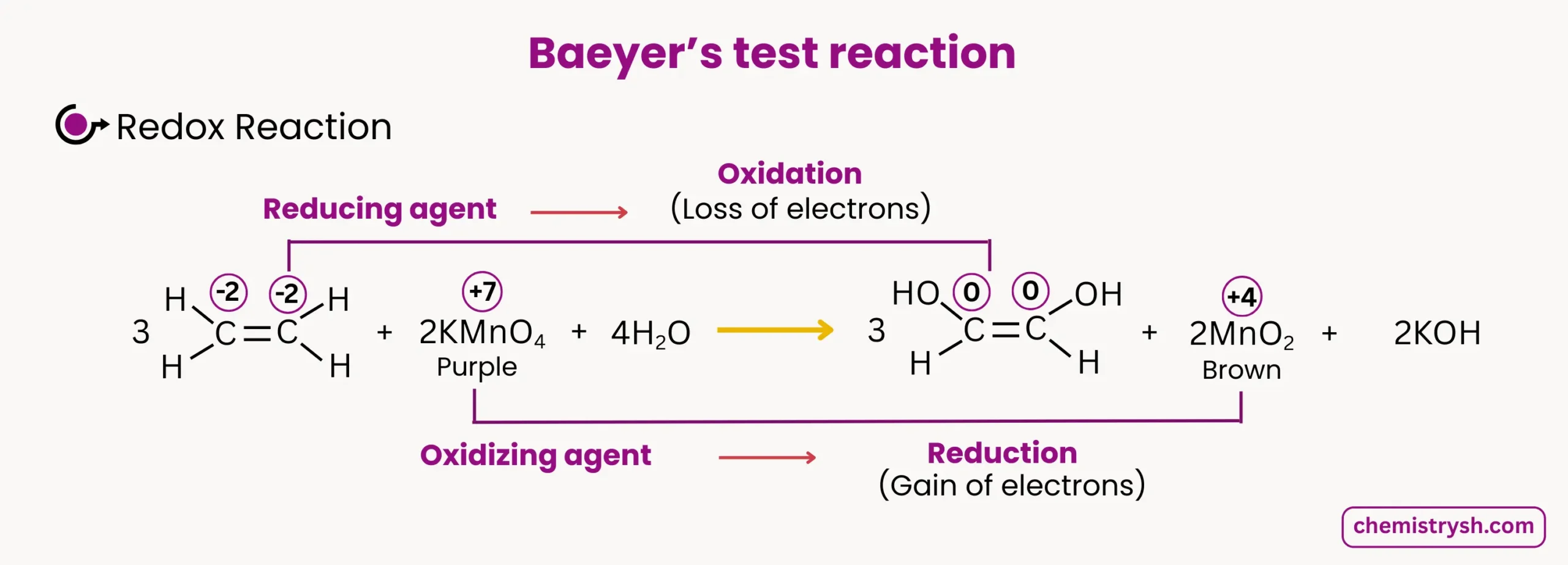
1. Alkene Oxidation
Ethene reacts with KMnO₄ in alkaline solution:
- Color change: Purple → Brown precipitate
- Oxidation state change: Mn⁷⁺ → Mn⁴⁺
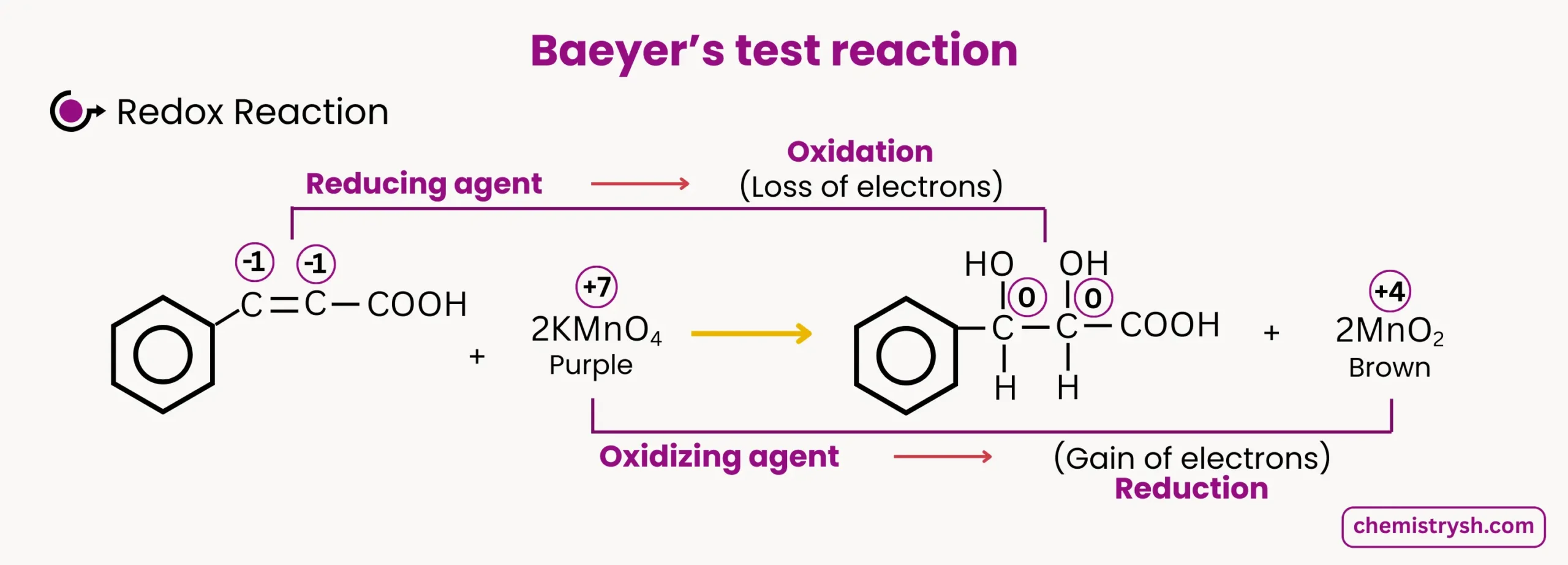
Similarly if cinnamic acid reacts with KMnO₄, it’s (C-C) double bond part get oxidized forming Diol and KMnO₄ (purple) reduce to MnO₂ (Brown ppt) .
2. Aldehyde Oxidation
Benzaldehyde oxidation by KMnO₄:
- Color change: Purple → Colorless or Brown
- Oxidation state change: Mn⁷⁺ → Mn⁴⁺
Behavior of KMnO₄ in Different Media
|
Medium |
Reaction |
Observation |
Oxidation State Change |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Acidic |
Strong oxidizing agent; reacts with most reducing agents, aldehydes, and some metals. |
KMnO₄ (purple) → Mn²⁺ (colorless/pale pink) |
Mn⁷⁺ → Mn²⁺ |
Oxidation of Fe²⁺ to Fe³⁺; aldehyde → acid |
|
Basic / Alkaline |
Reacts with alkenes, aldehydes, and some other oxidizable organic compounds. Forms diols from alkenes. |
KMnO₄ (purple) → MnO₂ (brown precipitate) |
Mn⁷⁺ → Mn⁴⁺ |
Ethene → ethane-1,2-diol; benzaldehyde → benzoic acid |
|
Neutral / Nutrient Solution |
Reacts slowly or selectively with oxidizable compounds; often used in biological or aqueous systems to test mild oxidation. |
KMnO₄ (purple) may fade slowly; sometimes brown MnO₂ forms |
Mn⁷⁺ → Mn⁴⁺ (slow) |
Mild oxidation of glucose or alcohols in aqueous solution |
Explanation:
- Acidic medium: KMnO₄ is a very strong oxidizer and is reduced completely to Mn²⁺, commonly used in titrations (permanganometry).
- Alkaline medium: KMnO₄ oxidizes alkenes to diols or aldehydes to acids, forming MnO₂ as a brown precipitate; this is the basis of the Baeyer test.
- Neutral / aqueous (nutrient solution): Oxidation occurs slowly and selectively, useful in mild reactions or biological/aqueous systems.
Materials and Reagents
- Potassium permanganate solution (1–2% aqueous)
- Sodium carbonate (alkaline medium)
- Organic sample
- Test tubes and droppers
Step-by-Step Procedure
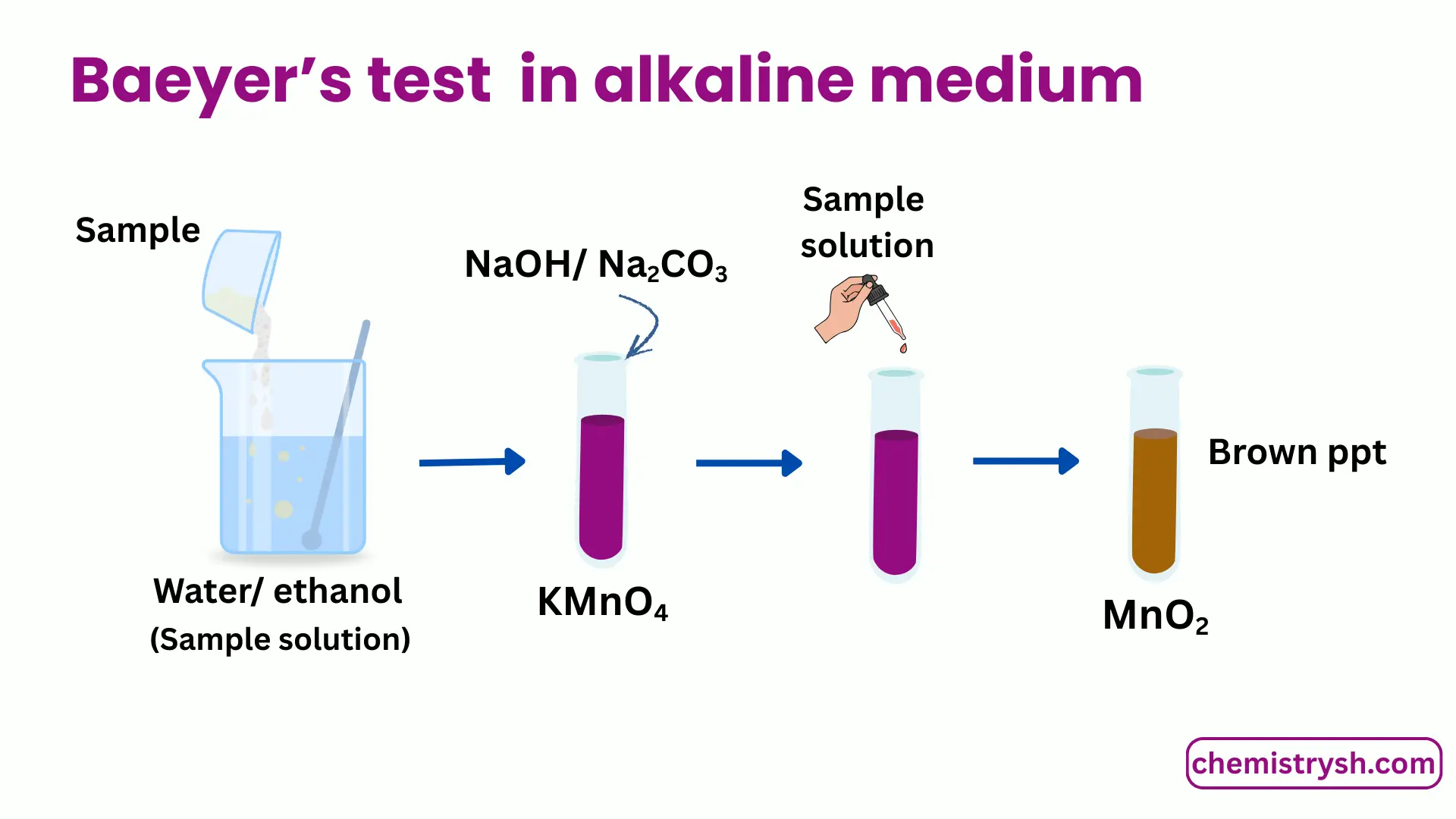
For alkaline medium
- Dissolve a small amount of the organic compound in water or aqueous ethanol.
- Prepare an alkaline KMnO₄ solution using sodium carbonate.
- Add KMnO₄ solution dropwise to the sample.
- Shake gently and observe any color change.
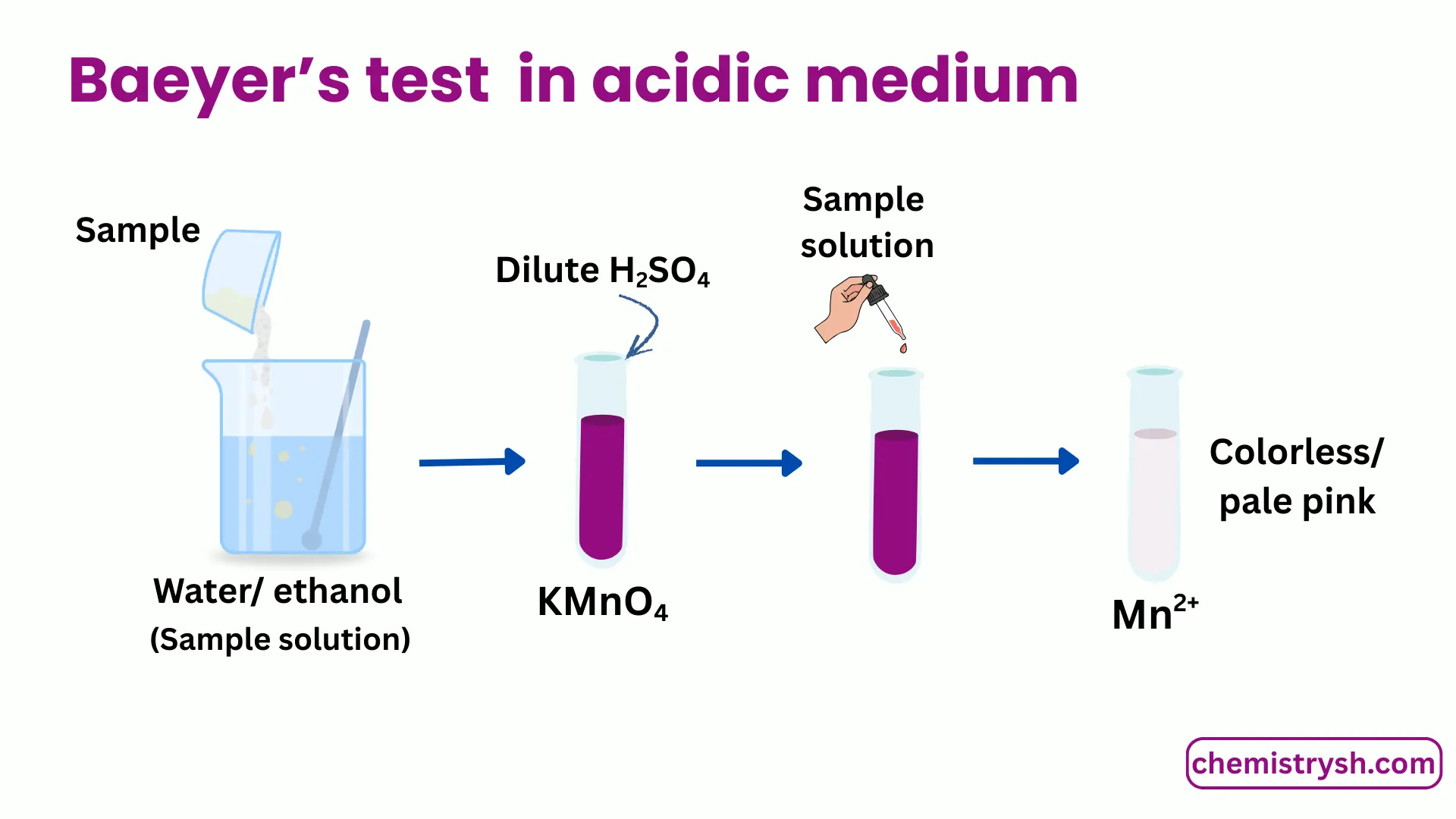
For acidic medium
- Dissolve a small amount of the organic compound in water or aqueous ethanol.
- Prepare an acidic KMnO₄ solution using sulfuric acid.
- Add KMnO₄ solution dropwise to the sample.
- Shake gently and observe any color change.
Observation and Interpretation
|
Purple → Brown/Colorless |
Positive KMnO₄ test; unsaturation or aldehyde present. |
|
Purple remains |
Negative KMnO₄ test; no reaction. |
Example of Positive results:
- Alkenes: Rapid decolorization with brown MnO₂ formation.
- Aldehydes: Gradual decolorization as aldehydes oxidize to carboxylic acids.
Comparison of Bromine Water Test and KMnO₄ Test
|
Feature |
Bromine Water Test (Br₂/H₂O) |
KMnO₄ Test (Baeyer Test) |
|---|---|---|
|
Purpose |
Detects unsaturation (C=C, C≡C) in organic compounds |
Detects unsaturation (C=C) and oxidizable functional groups (aldehydes, alcohols) |
|
Reaction Type |
Electrophilic addition across double/triple bonds; substitution with activated aromatics (phenols, anilines) |
Oxidation: Alkenes → diols; Aldehydes → carboxylic acids |
|
Observation |
Bromine color (brownish-red) disappears if double/triple bond present |
Purple KMnO₄ decolorizes; brown MnO₂ precipitate forms |
|
Reactivity with Aromatics |
Activated aromatics undergo electrophilic substitution |
Aromatics generally do not react under normal conditions |
|
Medium Required |
Usually neutral or slightly aqueous |
Alkaline medium for unsaturation; acidic medium for strong oxidation |
|
Example Reaction |
Ethene + Br₂ → 1,2-dibromoethane Phenol + Br₂ → 2,4,6-tribromophenol |
Ethene + KMnO₄ → ethane-1,2-diol Benzaldehyde + KMnO₄ → benzoic acid |
Precautions
- Use freshly prepared KMnO₄ solution.
- Maintain alkaline conditions.
- Avoid contamination with other oxidizable substances.
- Handle KMnO₄ with care; it is a strong oxidizing agent.
Applications
- Educational Laboratories: Detect unsaturation and aldehydes in organic samples.
- Research & Industry: Preliminary functional group analysis.
- Organic Synthesis: Confirm presence of C=C bonds.
Multiple Choice Questions
MCQ 1
1. What is the oxidation state of manganese in potassium permanganate?
A. +2
B. +4
C. +6
D. +7
MCQ 2
2. What forms on a positive Tollens Test?
A. Mn²⁺
B. MnO₂
C. MnO₄²⁻
D. MnO₄³⁻
MCQ 3
3. A positive KMnO₄ test with an organic compound indicates:
A. Saturated hydrocarbon
B. Unsaturation or aldehyde
C. No reaction
D. Aromatic ring
MCQ 4
4. KMnO₄ is reduced from Mn⁷⁺ to:
A. Mn²⁺
B. Mn³⁺
C. MnO₂
D. MnO₄²⁻
MCQ 5
5. KMnO₄ test is performed in:
A. Acidic medium
B. Neutral only
C. Alkaline medium
D. Any medium
MCQ 6
6. A compound that does not decolorize KMnO₄ is:
A. Ethene
B. Benzaldehyde
C. Hexane
D. 1‑butene
Viva questions
- What is the KMnO₄ (Baeyer) test used for?
- Why does the purple color of KMnO₄ disappear in a positive test?
- What product indicates a positive KMnO₄ test?
- How does KMnO₄ oxidize alkenes?
- What reagent is used to make KMnO₄ alkaline?
- How do you differentiate between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons using KMnO₄?
- What happens to aldehydes when treated with KMnO₄?
- Why must the KMnO₄ solution be fresh?
- What observation confirms a negative KMnO₄ test?
- Why is the test carried out in alkaline rather than acidic medium?
FAQ’s
Conclusion
The KMnO₄ Test is an effective and rapid qualitative method for detecting carbon–carbon unsaturation in alkenes and alkynes. The test operates through oxidative decolourisation of purple potassium permanganate to brown manganese dioxide, providing a clear visual indication of unsaturation. It remains a fundamental tool in organic chemistry for preliminary analysis and identification of unsaturated compounds.
References
- Vogel, A. I. Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition, Longman, 1989, pp. 345–348.
- Furniss, B. S., Hannaford, A. J., Smith, P. W. G., & Tatchell, A. R. Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition, Prentice Hall, 1989, pp. 343–347.
- Mendham, J., Denney, R. C., Barnes, J. D., & Thomas, M. J. K. Vogel’s Textbook of Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 6th Edition, Pearson, 2000, pp. 456–458.
- Ahluwalia, V. K., & Aggarwal, R. Comprehensive Practical Organic Chemistry, Universities Press, 2000, pp. 231–233.