The litmus paper test is a fundamental qualitative analysis technique used in organic chemistry to determine the acidic, basic, or neutral nature of organic compounds. It is particularly useful for water-soluble organic compounds, such as carboxylic acids, amines, and neutral molecules, where conventional indicators or more sophisticated pH measurements may not be immediately necessary.
This test helps college and university students quickly assess the chemical behavior of compounds in laboratory settings, providing a first-level insight into their functional group characteristics.
- Litmus paper test is only applicable when the compound is water soluble.
- If the compound is not water soluble, litmus paper test cannot be applied.
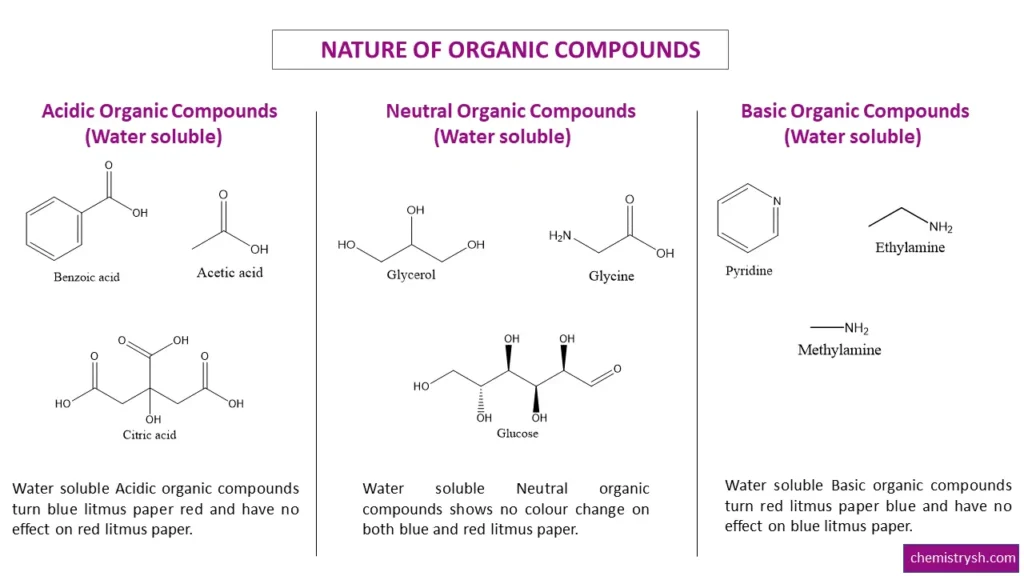
What Is Litmus Paper?
Litmus paper is specially treated paper impregnated with a natural dye obtained from lichens. It exists in two forms:
- Red litmus paper – sensitive to basic solutions.
- Blue litmus paper – sensitive to acidic solutions.
The dye undergoes a reversible color change depending on the pH of the solution it contacts, making it an effective acid-base indicator.
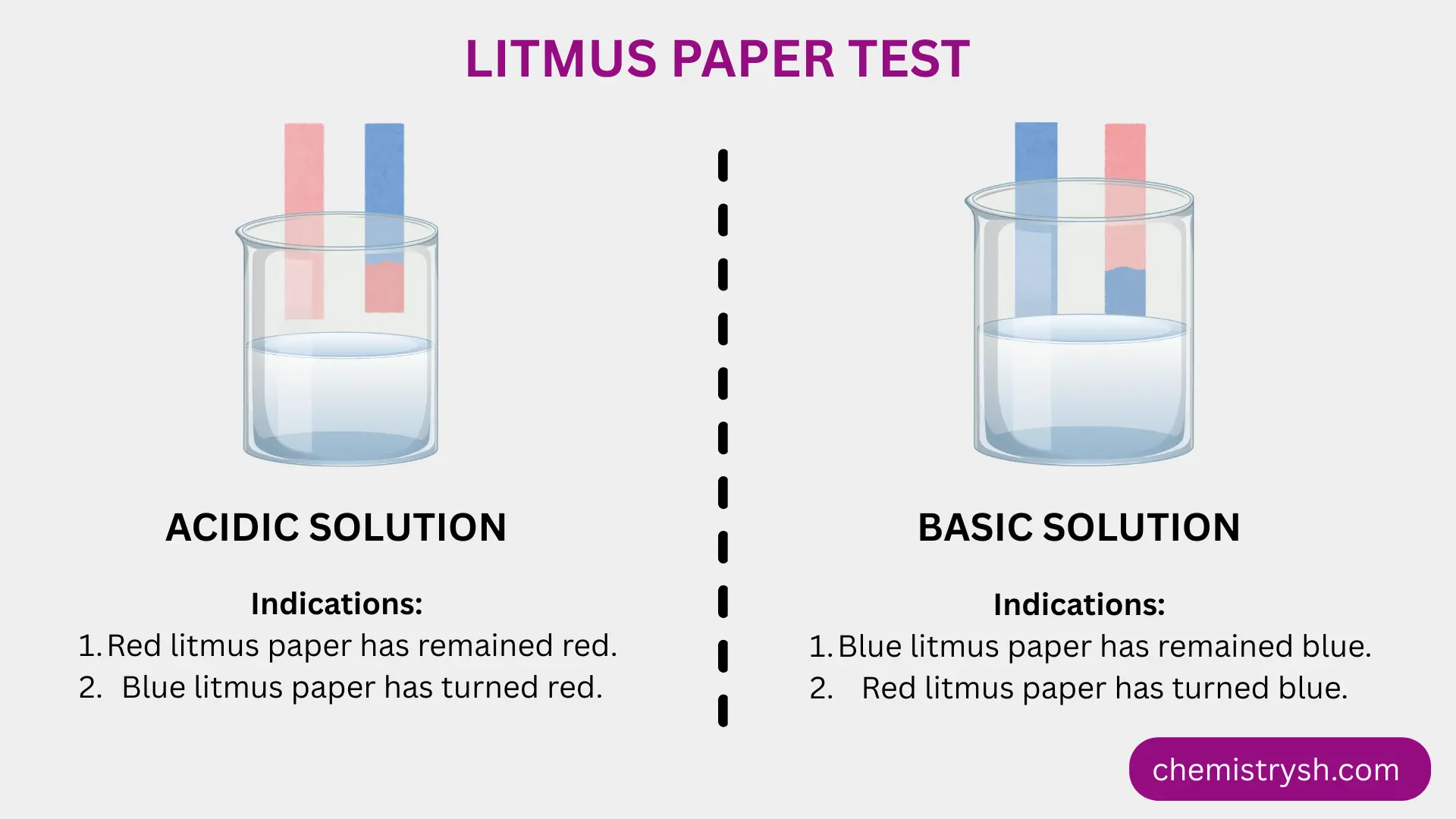
Principle of the Litmus Paper Test
The litmus paper test is based on the principle that acids and bases alter the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution, which can be detected by a color change in the litmus dye:
- Acidic organic compounds donate protons (H⁺) in solution, turning blue litmus red.
- Basic organic compounds, such as amines, accept protons from the medium, turning red litmus blue.
- Neutral organic compounds do not significantly change the pH and cause no color change in either litmus paper.
This simple chemical test provides a rapid and qualitative indication of the acidic or basic nature of soluble organic compounds
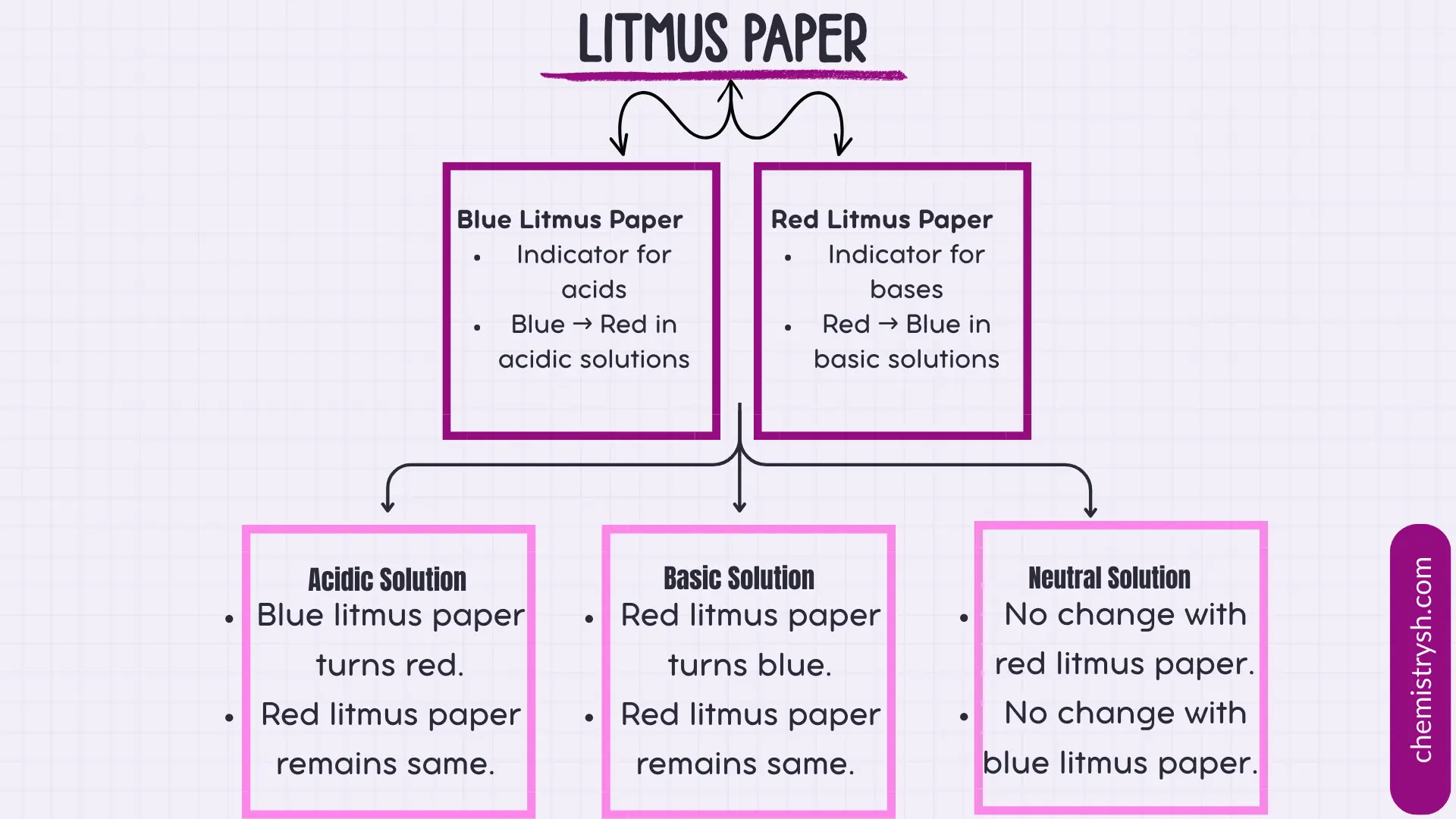
Scope of Litmus paper test in identifying Organic Compounds
The litmus test is particularly applicable to:
- Acidic organic compounds: Carboxylic acids, phenols, sulfonic acids.
- Basic organic compounds: Amines and other nitrogen-containing bases.
- Neutral organic compounds: Alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, and most hydrocarbons (provided they are soluble in the medium).
Materials Required for Litmus paper test
- Blue and red litmus paper strips
- Soluble organic compound sample
- Solvent (water or appropriate polar solvent)
- Test tube or small container
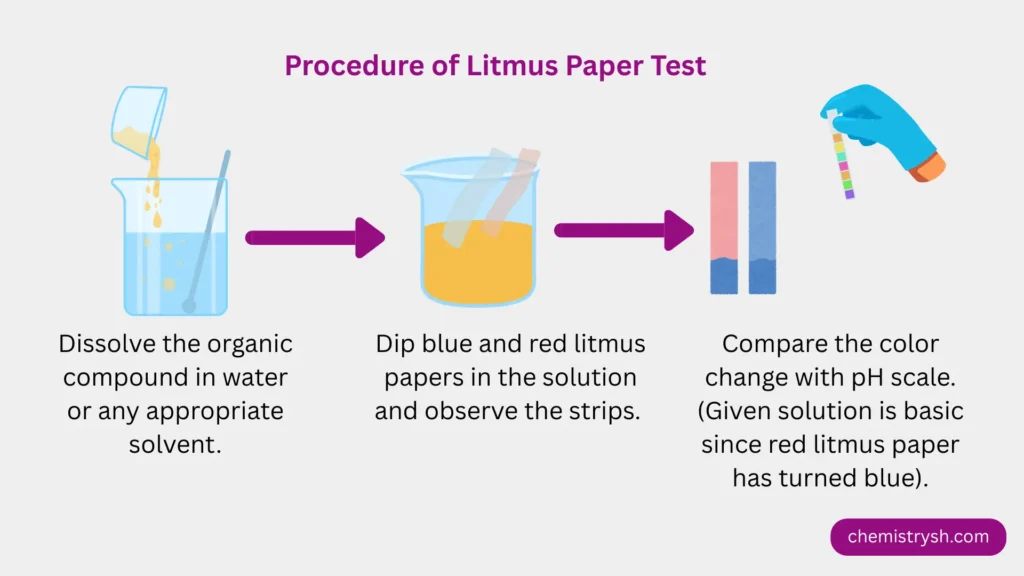
Procedure for performing Litmus paper test
- Dissolve a small amount of the organic compound in water or an appropriate solvent.
- Dip blue litmus paper into the solution and observe any color change.
- Dip red litmus paper into the solution and observe any color change.
- Compare the observations with the litmus color chart to classify the compound as acidic, basic, or neutral.
Advantages of the Litmus Paper Test
- Rapid, qualitative assessment of organic compounds.
- Useful as a preliminary test before detailed functional group analysis.
- Requires minimal equipment and preparation
Limitations of Litmus paper test
- Cannot provide exact pH values.
- Limited to soluble compounds. Insoluble organic compounds give unreliable results.
- The test does not differentiate weak acids or weak bases effectively.
- Color interpretation can sometimes be subjective for dilute solutions.
Comparison of Litmus paper with other indicators
|
Indicator |
Application in Organic Chemistry |
Advantage |
|---|---|---|
|
Litmus Paper |
Soluble acids/bases |
Quick, simple, qualitative |
|
Universal Indicator |
Wide pH range of soluble compounds |
Approximate pH value |
|
Universal Indicator |
Wide pH range of soluble compounds |
Quantitative and precise |
Practical Applications of Litmus paper test
- Laboratory experiments: Identifying carboxylic acids, amines, and neutral compounds.
- Teaching organic chemistry: Illustrates proton donation/acceptance in functional groups.
- Quick qualitative screening: Prior to advanced techniques like titration or spectroscopy.
Conclusion
The litmus paper test remains a foundational tool in organic chemistry for differentiating acidic, basic, and neutral compounds, particularly when they are soluble. While qualitative, it provides essential first-hand insight into the chemical nature of compounds, helping students and chemists plan further analytical or synthetic procedures.
Viva questions
- What is litmus paper?
- Which natural source is used to prepare litmus?
- What is the color of blue litmus paper in an acidic solution?
- What happens when red litmus paper is placed in a basic solution?
- Does litmus paper show any change in a neutral solution?



